Thursday, May 27, 2021
Monday, May 24, 2021
Sunday, May 23, 2021
Mucormycosis
Mucormycosis is a fungal infection caused by
molds (mucormycetes). These fungi are present in soil and in decaying organic
matter e.g., compost, rotten woods, dungs etc. Spores of these fungi are present
throughout in the environment. When any person with health issues (e.g., diabetes
etc.) and weak immunity come in contact with fungal spores they get mucormycosis.
Types
of mucormycosis
1. Rhinocerebral (sinus and
brain) mucormycosis: this infection spread to the
brain from sinuses and most common in persons with uncontrolled diabetes and in persons who have had a
kidney transplant.
Symptoms- One-sided
facial swelling, headache, nasal or sinus congestion, black lesions on nasal
bridge or upper inside of mouth that quickly become more severe, fever.
2. Pulmonary (lung)
mucormycosis: this is the most common infection in cancer
patient and in person who have had organ transplant.
Symptoms- Fever,
Cough, Chest pain, shortness of breath.
3. Gastrointestinal
mucormycosis: this infection is common in
lower age group people who have weak immunity.
Symptoms- Abdominal
pain, nausea and vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding.
4. Cutaneous (skin) mucormycosis: spores enter in the body through skin. When any break in the
skin occurs (by injury etc.) spores of fungi get entered in the body through
broken skin.
Symptoms- Blisters
or ulcers, infected area may turn black, pain excessive redness, swelling
around the wound.
5. Disseminated mucormycosis: in this
infection spores transport through bloodstream to different organs. Brain is the commonly affected part; it can also affect spleen and
heart.
Symptoms- Mental
status changes, coma.
Causative
agent:
Rhizopus species, Mucor species, Rhizomucor species, Syncephalastrum species, Cunninghamella
bertholletiae, Apophysomyces species, and Lichtheimia (formerly Absidia) species.
Treatment
Mucormycosis is treated by antifungal medicine like amphotericin B (intravenous),
posaconazole (intravenous/oral), or isavuconazole (intravenous/oral). Often,
mucormycosis needed surgery to remove the infected part.
Thursday, May 13, 2021
2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG): A Weapon Against COVID-19
Nowadays, everyone is talking about 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG).
Institute
of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences (INMAS), a lab of Defense Research and
Development Organization (DRDO) has developed the therapeutic application of
2-DG against COVID-19 in collaboration with its industry partner Dr. Reddy’s
Laboratories (DRL). It is being claimed that 2-DG will help COVID-19 patients in fast recovery. The results of its clinical
trial were very positive and encouraging therefor, DCGI approves anti-COVID drug developed by DRDO for
emergency use.
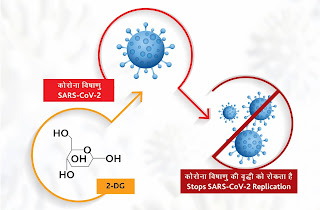
2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) is the analog of glucose in which 2-OH is replaced by –H. As we know that glucose is the main source of energy in living beings and generate energy by breakdown of it. Glucose enters in energy producing metabolic pathway through glycolysis. In first step of glycolysis glucose is converted into glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P) by hexokinase enzyme.
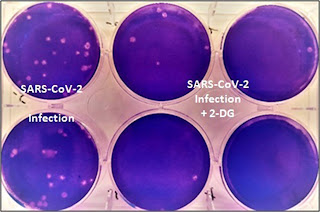
When 2-DG is presented in cells it phosphorylated by hexokinase to 2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate (2-DG-P). 2-DG-P is not recognized by glycolytic enzymes and further metabolism of glucose cannot occur. We can say that 2-DG is a glycolytic inhibitor. Consequently, energy (ATP) production is stopped because end product of glycolysis (pyruvic acid) is the fuel for further energy producing pathways. Therefore, accumulation of 2-DG-P and depletion of ATP occur. In the same way it acts on COVID-19 infected cells. It accumulates in the virus infected cells and prevents virus growth by stopping viral synthesis and energy production.
Some images are attached here released by Press Information Bureau, Government of India.
Real Time PCR and its Application in Plant Pathology-III
Relevant Features of Real-Time PCR Rapidity : Compared with classical PCR, real-time PCR is rapid to provide reliable data. T...
-
Combination of alleles in any organims is known as its genotype. An allele is one of two or more alternate forms of a gene located at the...
-
Structure of Coronavirus: (Image source: Stephen N.J. Korsman et al. (2012). Human coronaviruses . Virology (2012): 94-95) Life...
-
The genes responsible for the transfer of the T-DNA region into the host plant are also situated on the Ti plasmid in a region of approxim...